Question
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:

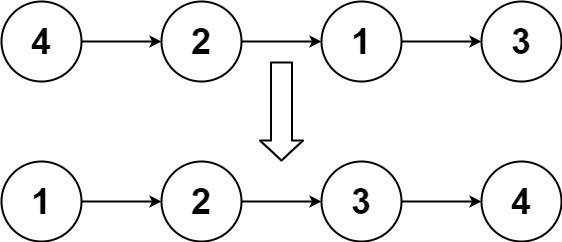
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Solution
Approach
 Merge Sort
Merge Sort
Complexity
- Time complexity:$O(nLog(n))$
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| # Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
### Simulation Process ###
# [4-> 2-> 1-> 3]
# 4, 4-> 1, 2-> None, 1
# l, r = sort(4->1), sort(3)
# sort(3)
# [3]
# sort(4->1)
# [4-> 2-> 1]
# 4, 4-> 1, 2
# l, r = sort(1->2), sort(None)
###########################
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
# use two pointer to find the mid point for Merge Sort
fast = slow = head
while fast.next.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if not fast.next:
break
start = slow.next
slow.next = None
l, r = self.sortList(head), self.sortList(start)
return self.merge(l, r)
def merge(self, l, r):
if not l or not r:
return l or r
head = tmp = ListNode(0)
while l and r:
if l.val <= r.val:
tmp.next = l
l = l.next
else:
tmp.next = r
r = r.next
tmp = tmp.next
if l:
tmp.next = l
if r:
tmp.next = r
return head.next
|